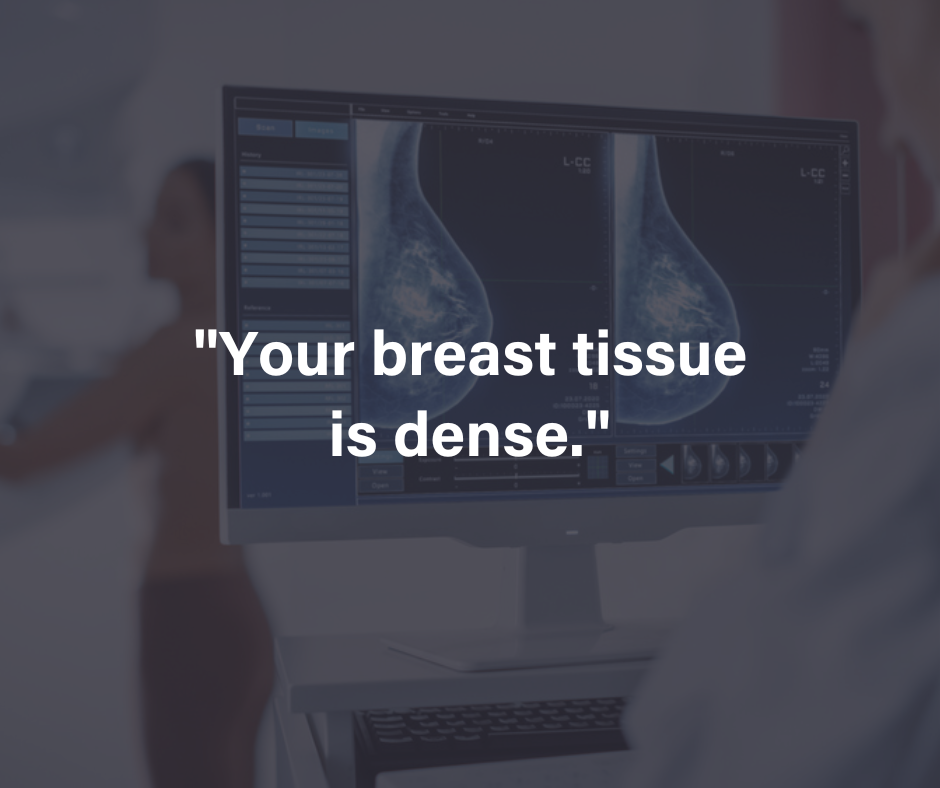
If a mammogram shows you have dense breast tissue, you may wonder what that means for your breast cancer risk. Dense breasts typically make it difficult for radiologists to see cancer through a mammogram. As a result, your radiologists may not detect cancer until it’s grown too big. However, having dense breasts doesn’t always mean you will have breast cancer, but they are a risk factor you should consider when assessing your breast cancer risk. With MagView’s mammography tracking solutions, doctors can follow up on your mammograms and determine the next appropriate steps to take. In this post, we will discuss everything you need to know about breast density levels.
Identifying Dense Breasts
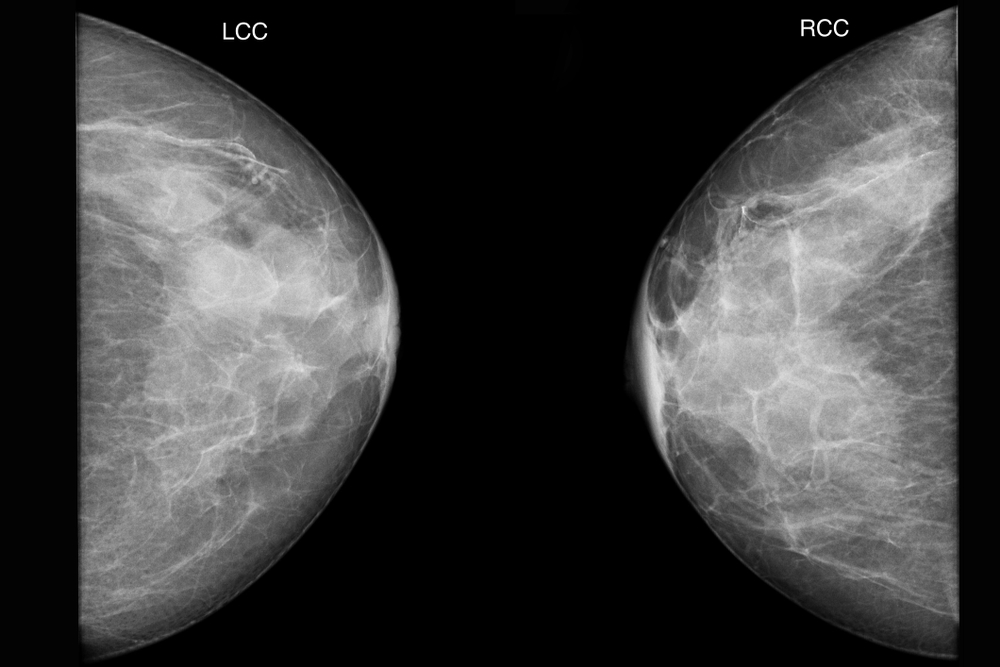
When a doctor says you have dense breasts, they simply mean your breast tissue contains more glandular (milk ducts) and supportive or fibrous tissue that breasts with mostly fatty tissue. If your doctor says you have non-dense breast tissue, that means your breast contains more fatty tissue than glandular and fibrous tissues. On a mammogram, non-dense tissue appears transparent and darker. Whereas, dense breast tissue appears as a solid white area on a mammogram, making it a challenge to see through.
Dense breasts are quite common. According to the CDC, nearly half of all women above 40 years old have dense breasts. You cannot feel dense breasts. The only way to know if you have dense breasts is to have a mammogram.
What Are the Four Categories of Breast Density?
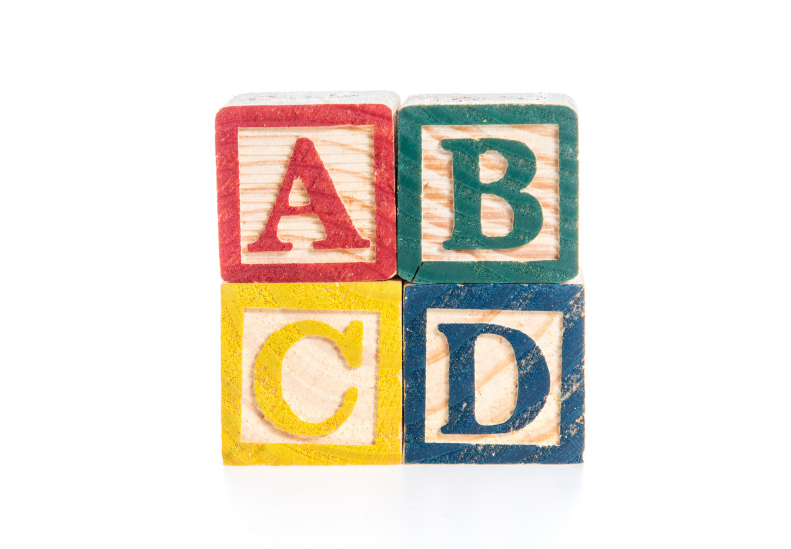
Radiologists who analyze your mammogram determine the density ratio in your breast tissue. Once they check the ratio of dense tissue to non-dense tissue, they assign a level of breast density. In your report, radiologists will assign your breast density to one of the following categories:
- A: 10% of women have breasts that are entirely fatty
- B: 40% of women have a few areas of dense tissue scattered across the breast (low levels of fibro glandular breast tissue
- C: 40% of women have breasts that are evenly dense throughout (many areas of fibrous and glandular tissue in the breast
- D: 10% of women have breasts that are extremely dense
If your mammogram says you have dense breasts, it means you have heterogeneously dense or extremely dense breast tissue. The density levels are described using a result reporting system called Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS).
How Do Dense Breasts Affect Breast Cancer Detection?
The main reason why breast density matters is that it hinders proper mammogram reading. That means cancer can go undetected in a mammogram. Dense breasts have also been shown to increase your risk of breast cancer.
What Factors Affect Breast Density?
Most women have dense breasts due to their genetics. Other factors that may increase your breast density are:
- Being pregnant or breastfeeding
- Taking hormone replacement therapy
- Having a low body weight
- Being young
Questions To Ask Your Doctor if You Have Dense Breasts
If your doctor has told you that you have dense breasts, you may want to know the way forward. Asking questions will help you understand the most appropriate steps to take for your breast health. Some of the questions you can ask include the following:
- What is my breast density according to the mammogram?
- Do you recommend additional screening or diagnostic tests for me?
- What is my overall cancer risk, given that dense breasts are part of the risk?
Based on your mammogram report, your doctor will determine whether you need additional imaging or testing. You can also use our IBIS risk assessment calculator to check your breast cancer risk.











![monitoring breast density shutterstock_1299510538-[Converted]](https://magview.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/shutterstock_1299510538-Converted.jpg)