Breast density is an important factor in understanding your breast health. Dense breast tissue can make it harder to detect potential abnormalities on a mammogram. This guide will help you understand what dense breast tissue is, what causes dense breast tissue, how it affects your screening, and what questions to ask your doctor.
What is Dense Breast Tissue?
Understanding dense breast tissue is key to interpreting mammogram results and ensuring the most accurate screening for breast health.
Definition and Explanation
Dense breast tissue refers to the appearance of your breast on a mammogram. Breasts are made up of fatty tissue, glandular tissue, and connective tissue. Women with dense breasts have more glandular and connective tissue and less fatty tissue. This makes the breast appear whiter on a mammogram, which can sometimes hide abnormalities like tumors.
What causes dense breast tissue?
Several factors can influence breast density, including:
- Age: Younger women are more likely to have dense breast tissue and it tends to decrease with age.
- Genetics: A family history of dense breast tissue or breast cancer may increase the likelihood of having dense breasts.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormone levels, especially during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause, can affect breast density.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Women using hormone replacement therapy, particularly estrogen, may experience increased breast density.
- Body Weight: Women with lower body fat tend to have denser breast tissue compared to those with higher body fat.
- Lifestyle Factors: Some studies suggest that factors like alcohol consumption or a high-fat diet may play a role in breast density.
Signs and Symptoms of Dense Breast Tissue
There are no physical signs or symptoms of dense breast tissue. It cannot be felt during a self-exam, and having dense breasts does not cause pain or discomfort. The only way to identify dense tissue is through imaging, such as a mammogram.
How to Determine Breast Density
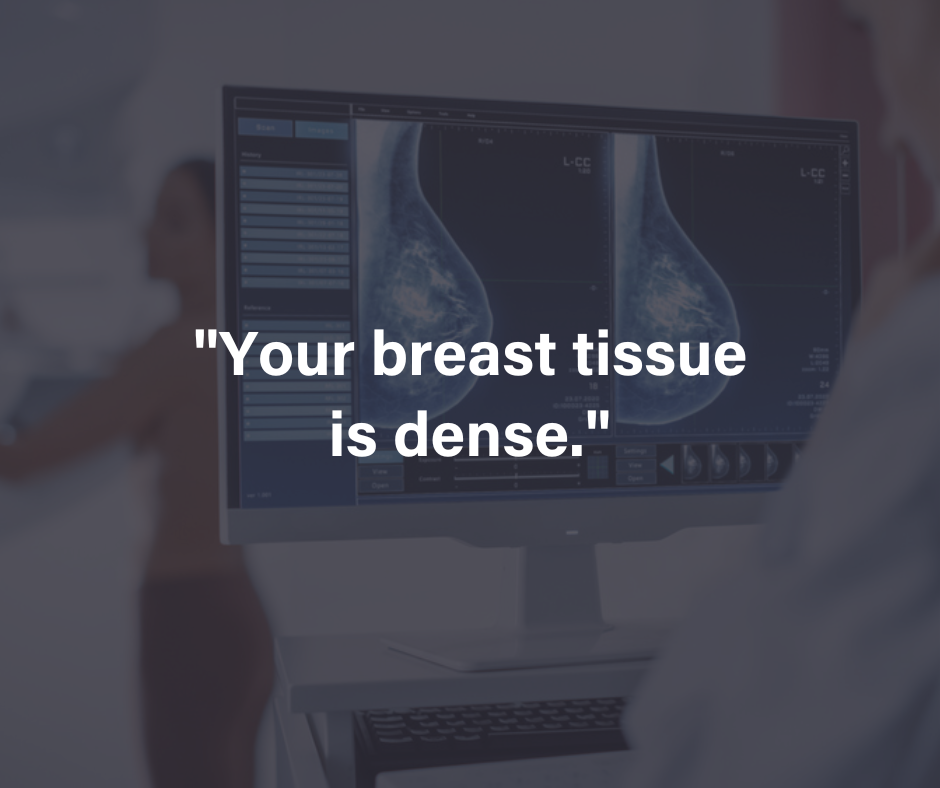
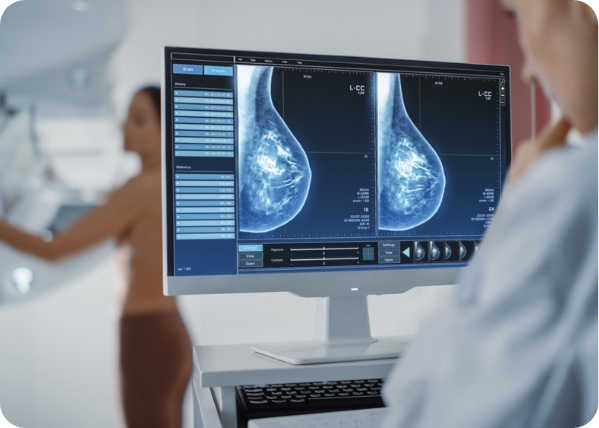
You can’t tell if you have dense breasts by how they feel. After a mammogram, your doctor or radiologist will assess your breast density and categorize it based on a scale from the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS). This system classifies breast density into four categories: almost entirely fatty, scattered areas of fibroglandular density, heterogeneously dense, and extremely dense.
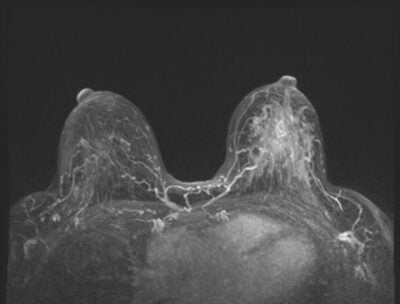
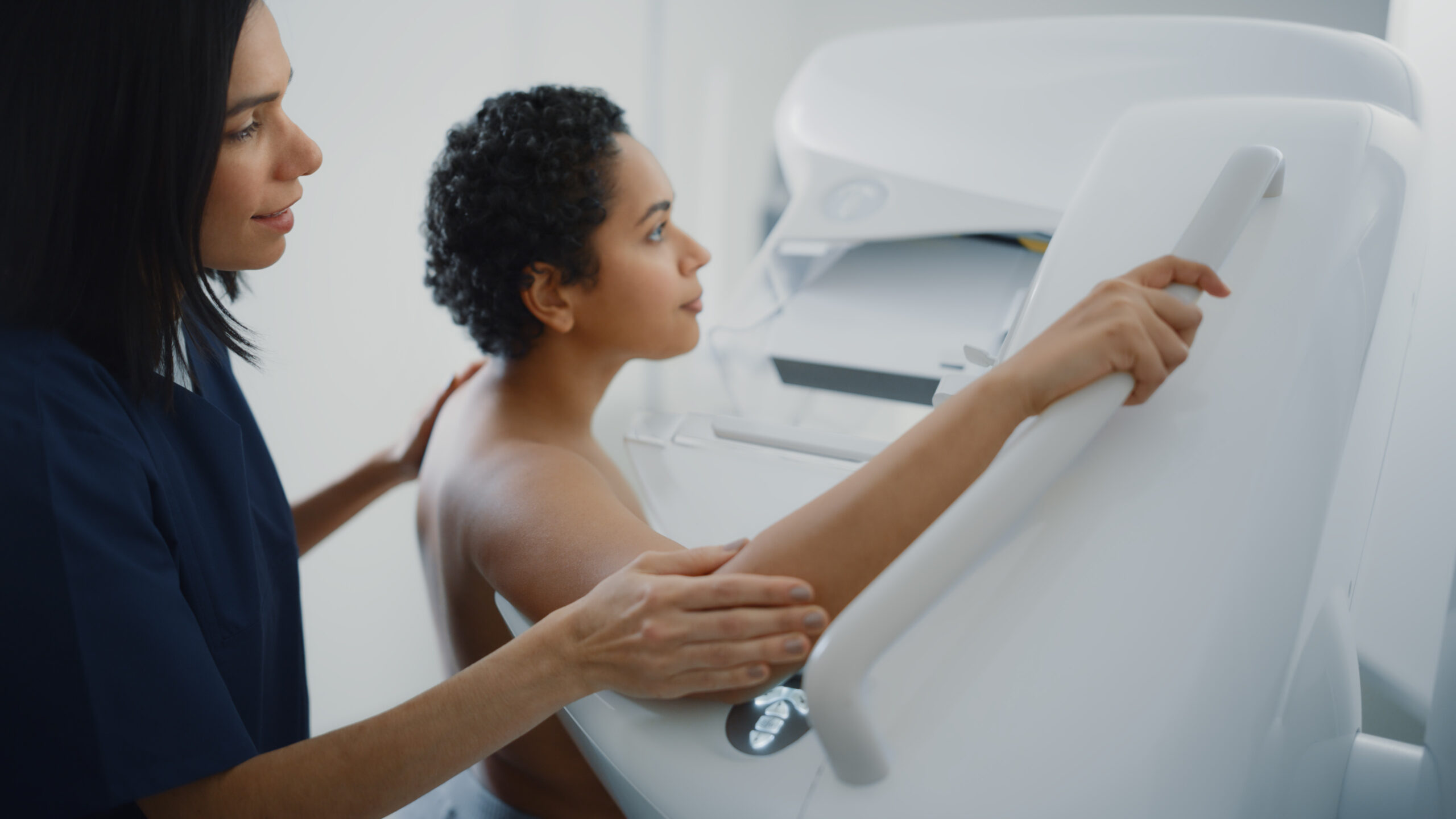
Mammograms and Ultrasound
Dense breast tissue can make mammogram results less clear, as both dense tissue and potential tumors show up as white on the images. This similarity can make it harder to detect abnormalities and might require additional screening.
Impact of Dense Breast Tissue on Screening Accuracy
- Dense tissue can mask small tumors, reducing the effectiveness of standard mammograms in early cancer detection.
- This often results in the need for follow-up tests to ensure nothing is missed.
Additional Screening Options
To overcome these challenges, alternative imaging techniques are often recommended:
- Ultrasound: Effective for detecting abnormalities not easily seen on mammograms.
- 3D Mammography: Takes multiple images from different angles, offering a more detailed view of breast tissue, making it easier to spot hidden issues.
Discussing Breast Density with Your Doctor
Having dense breast tissue is common, but it’s important to understand how it affects your breast health and what steps you should take next. A conversation with your doctor can help clarify any concerns and ensure that you’re getting the right care.
Key Questions
Some questions you might want to ask include:
- What does it mean for me to have dense breast tissue?
- Do I need additional screening tests like ultrasound or 3D mammography?
- How often should I have mammograms or other screenings given my breast density?
- Are there lifestyle factors that influence breast density?
Next Steps
After discussing your breast density with your doctor, here are a few simple steps you might take:
- Schedule additional screenings: Your doctor may recommend follow-up tests like an ultrasound or MRI if your mammogram results were unclear.
- Create a personalized screening plan: Based on your breast density and risk factors, you may need more frequent or different types of screenings.
- Review lifestyle habits: Ask your doctor if any lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight or reducing alcohol intake, could help manage breast density.
- Stay informed: Keep track of any changes in your breast health and schedule regular follow-up appointments to monitor your condition.
Take Charge Of Your Health
Follow MagView’s women’s health blog for more information about breast cancer, mammograms, and other important women’s health issues.
References:
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Breast Density and Your Mammogram Report. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org
- National Cancer Institute. (2023). Breast Density. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Dense Breast Tissue: What It Means to Have Dense Breasts. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org



















![monitoring breast density shutterstock_1299510538-[Converted]](https://magview.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/shutterstock_1299510538-Converted.jpg)