Genetic testing for breast cancer is a valuable way to understand your risk, particularly if there’s a family history of the disease. While many cases of breast cancer occur randomly, some are tied to inherited gene mutations. Identifying these mutations can empower you to make proactive, informed decisions about your health, including whether genetic testing might be right for you and what to expect from the process.
What Is Genetic Testing?
Genetic testing is a medical tool used to identify DNA mutations that may increase your risk of diseases like breast cancer. Certain gene mutations are closely linked to a higher likelihood of developing breast and ovarian cancer.
Key Genes Linked to Breast Cancer
Genetic mutations in certain genes can increase the risk of breast cancer. Here are some of the most well-known genes associated with this risk:
- BRCA1: Mutations in this gene can significantly increase the risk of both breast and ovarian cancers.
- BRCA2: Similar to BRCA1, mutations in this gene are strongly associated with a higher risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
- PALB2: Mutations in this gene can moderately increase the risk of breast cancer.
- TP53: Known as the “guardian of the genome,” mutations in this gene are linked to several types of cancer, including breast cancer.
- ATM: Mutations in this gene are associated with a slightly increased risk of breast cancer.
Benefits of Knowing Your Genetic Risk
Understanding your genetic risk for breast cancer offers several advantages, empowering you to take control of your health and plan for the future:
- Informed Health Decisions: Knowing if you’re at higher risk allows you to take preventive measures or start early breast cancer screening.
- Family Planning: Genetic testing can help inform your family members of their potential risks.
- Tailored Treatments: Knowing their genetic profile can help select the most effective treatment options for those already diagnosed.
Who Should Consider Genetic Testing?
Genetic testing for breast cancer is often recommended for those with certain risk factors. Here are the primary factors to consider when deciding if testing is right for you.
- Family History of Breast or Ovarian Cancer: Women with a close family member (mother, sister, daughter) who had breast or ovarian cancer may be at increased risk.
- Personal History of Breast Cancer or Other Cancers: Women who have been diagnosed with breast cancer before the age of 50, or those with a personal history of other cancers, may benefit from genetic testing.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as Ashkenazi Jewish women, have a higher prevalence of BRCA mutations.
The Genetic Testing Process
The process of genetic testing is simpler than you might think. From sample collection to interpreting results, each step is designed to give you the knowledge you need to make informed health decisions.
What to Expect During Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is a straightforward process designed to provide valuable insights about your risk. Here’s an overview of what typically happens:
- Sample Collection: Testing is usually done via a blood sample or saliva sample, both of which are non-invasive and easy to provide.
- Analysis: The sample is sent to a laboratory where it is analyzed for mutations in the BRCA genes or other relevant genes.
- Results Timeline: Results typically take several weeks to be processed. Genetic counselors will often help interpret the results and discuss the next steps
The Role of Genetic Counseling Before and After Testing
For many women, genetic counseling is recommended to discuss the potential benefits and risks before undergoing genetic testing. A genetic counselor will help you:
- Understand the Testing Process: Genetic counselors explain the test, its purpose, and what the results might mean for you.
- Interpret Results: If you test positive for a mutation, a counselor will help you understand what it means for your health and the health of your family members.
- Develop a Plan: Based on the results, the counselor will help create a personalized health plan, including screenings, preventive measures, or treatment options.
Preventative and Follow-Up Measures
If you test positive for a genetic mutation, there are several preventive measures you can take to reduce your breast cancer risk. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are essential for those with a heightened risk for breast cancer.
Risk-Reduction Strategies
- Lifestyle Changes: Healthy habits like maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and limiting alcohol intake can help reduce your risk.
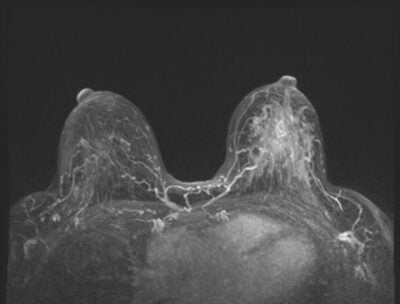
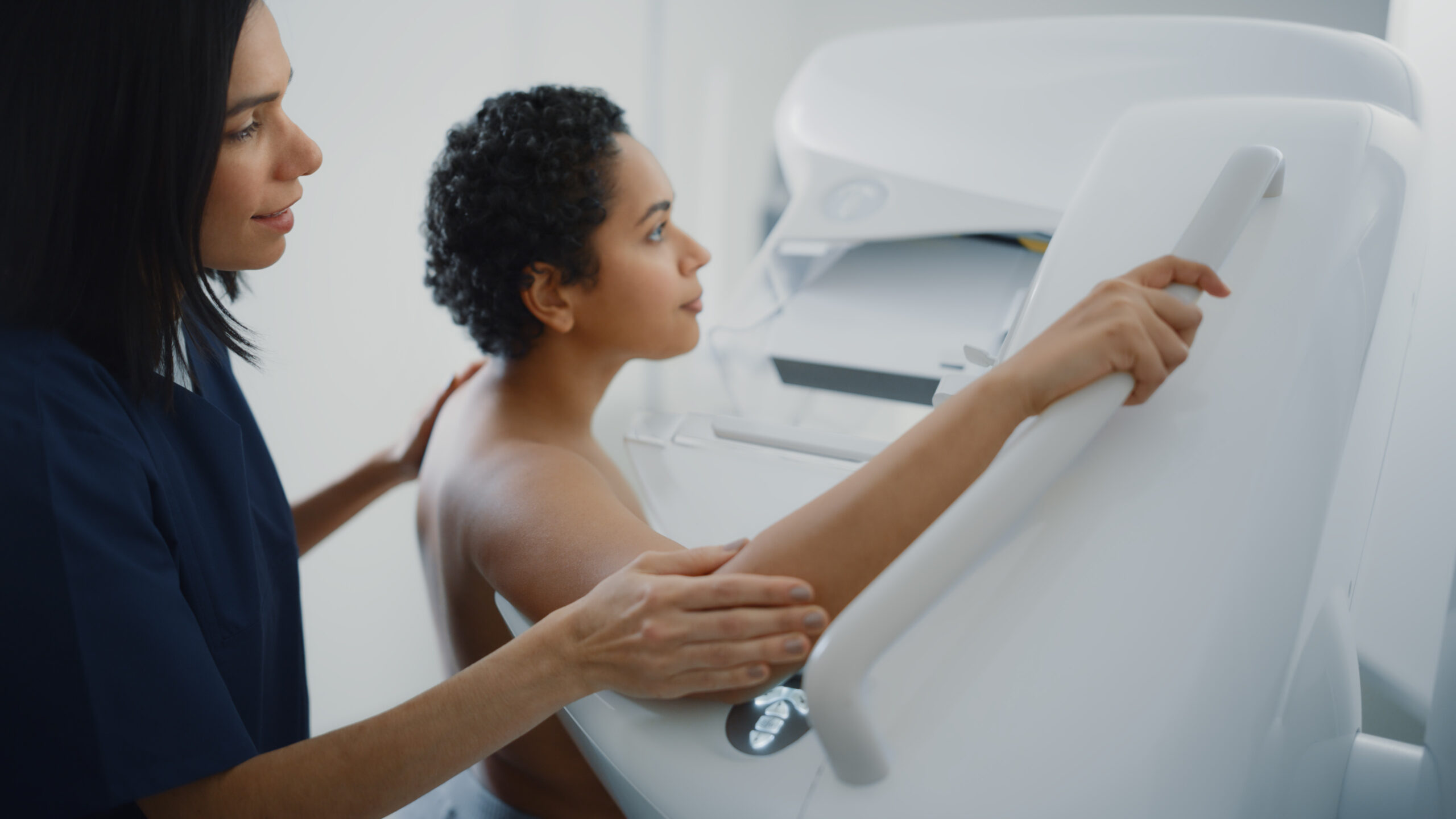
- Increased Medical Surveillance: For women with a genetic predisposition, early and more frequent breast cancer screenings (like mammograms and MRIs) may be recommended.
- Preventive Surgery: In some cases, women at high risk may choose preventive surgeries, such as prophylactic
mastectomy (removal of breasts) or oophorectomy (removal of ovaries), to reduce cancer risk.
Takeaway: Make an Informed Decision About Genetic Testing
Genetic testing for breast cancer is a powerful tool for understanding your risk and making proactive health decisions. If you have risk factors like a family history of breast cancer or early-onset breast cancer, consider discussing genetic testing with a healthcare provider. Knowing your genetic makeup can guide preventive actions, enhance early detection, and potentially save lives.
References
- https://www.breastcancer.org/genetic-testing
- https://www.komen.org/breast-cancer/risk-factor/gene-mutations-genetic-testing
- https://www.cdc.gov/breast-ovarian-cancerhereditary/testing/index.html
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa191394
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/breast-cancer/risk-and-prevention/breast-cancer-risk-factors-you-cannot-change.html




















![monitoring breast density shutterstock_1299510538-[Converted]](https://magview.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/shutterstock_1299510538-Converted.jpg)