Getting a mammogram can be nerve-wracking, and reading the mammogram results report afterward can feel confusing. In this guide, we’ll cover the essential parts of a mammogram report, including dense tissue, breast calcifications, and what abnormal mammogram results mean.
Decoding Mammogram Terminology
Mammograms are an important tool for detecting breast abnormalities, but the medical language used can be overwhelming.
Common Mammogram Terms and What They Mean
- Views Taken: Describes the different images or angles used during the mammogram, like craniocaudal (CC) and mediolateral oblique (MLO), which help give a more complete view of the breast.
- Breast Composition: This refers to how much fibrous and glandular tissue you have compared to fat. This information helps the radiologist understand the density of your breasts and how it may affect the ability to detect abnormalities.
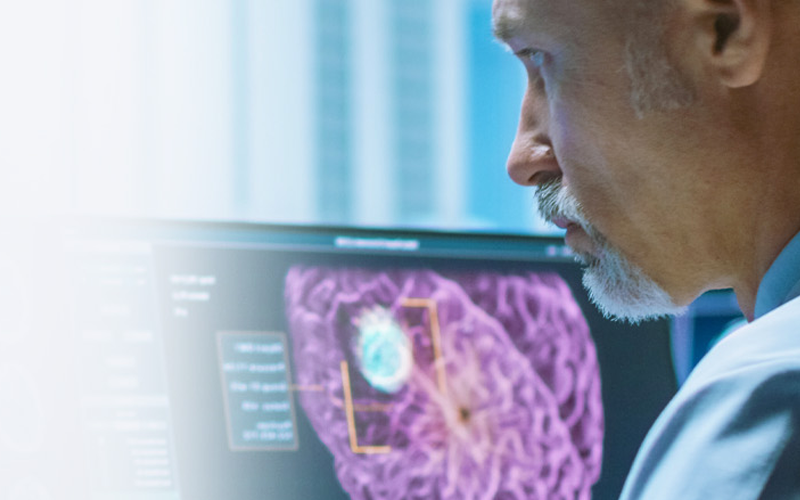
- Masses: An area that looks different from surrounding tissue. A mass can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Further tests, like a biopsy, might be recommended.
Key Areas to Review in Your Mammogram Report
When reviewing your report, these sections provide critical information for understanding your breast health and the next steps:
- BI-RADS Score: The BI-RADS score categorizes your results, indicating whether additional tests or follow-ups are needed. Scores range from 0 (incomplete) to 6 (confirmed cancer), with higher scores generally suggesting a need for further investigation.
- Impression/Assessment: This is the radiologist’s conclusion based on the images, summarizing what was found and whether anything requires follow-up. It’s a key section for understanding the overall results.
- Follow-Up Recommendations: Your report may recommend follow-up actions, which could range from routine monitoring to additional tests like ultrasound, MRI, or biopsy, depending on what was found.
Dense Tissue, Calcifications, and Masses
Each of these findings provides important insights into your breast health:
Dense Tissue: If your report mentions dense tissue, there is more fibrous and glandular tissue in the breast compared to fatty tissue. Dense breasts are not abnormal, but they can make it harder to spot potential cancers on a mammogram. Women with dense breasts might benefit from additional screening methods, like 3D mammograms or MRIs.
Breast Calcifications: Tiny calcium deposits in the breast. While most calcifications are harmless, certain patterns may suggest early-stage cancer and require further investigation. Depending on their appearance, your doctor might suggest a biopsy to determine if the calcifications are benign or malignant.
Masses: A mass refers to an area of tissue that looks different from surrounding tissue. It could be benign or malignant, and your doctor may recommend further tests like ultrasound or biopsy to determine the nature of the mass.
Understanding BI-RADS Classification
The BI-RADS system (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System) is used to classify mammogram results. This system helps your doctor understand how urgent follow-up actions should be.
What Each Category Indicates
- BI-RADS 1: No abnormalities. This means your mammogram is normal.
- BI-RADS 2: Benign findings. There are no signs of cancer, but the report mentions non-cancerous changes like cysts.
- BI-RADS 3: Probably benign. The findings are likely harmless, but a short-term follow-up mammogram is recommended to monitor any changes.
- BI-RADS 4: Suspicious abnormality. A biopsy is recommended to evaluate the abnormal area further.
- BI-RADS 5: Highly suggestive of malignancy. There is a strong chance of cancer, and immediate action, like a biopsy, is necessary.
Interpreting Abnormal Mammogram Results
If your report shows abnormal mammogram results, it’s important not to panic. Abnormal results do not always mean cancer, but they do require further investigation.
Next Steps and Follow-Up Actions
Depending on the nature of the abnormality, your doctor might suggest one or more of the following tests:
- Additional imaging: An ultrasound or MRI can provide more detailed images of the abnormal area.
- Biopsy: A small sample of tissue may be taken for analysis to determine whether the abnormality is cancerous or benign.
- Short-term follow-up: In some cases, your doctor may recommend a repeat mammogram in six months to see if there are any changes in the findings.
Discussing Your Report with Your Doctor
After reviewing your mammogram report, it’s important to have a thorough conversation with your doctor. Being prepared with the right questions can help you understand your results and decide on the next steps.
Questions to Ask and How to Prepare
- What does it mean if I have dense tissue, and should I consider additional screening?
- Are the breast calcifications in my report something to worry about?
- Do I need further testing, such as an ultrasound or biopsy?
- How should I monitor any findings that were marked as “probably benign”?
Stay Informed
Want to be better equipped to make informed decisions about your breast health? Follow MagView’s women’s health blog to learn more about breast cancer and other important women’s health issues from industry experts.
References:
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. (2023). Breast Cancer: Screening. Retrieved from https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org
- American College of Radiology. (2023). BI-RADS Atlas. Retrieved from https://www.acr.org
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Understanding Your Mammogram Report. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org




















![monitoring breast density shutterstock_1299510538-[Converted]](https://magview.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/shutterstock_1299510538-Converted.jpg)