Breast cancer awareness begins with taking proactive steps to safeguard your health. Understanding the available testing options, knowing when to start screening, and interpreting results can empower you to make informed decisions about your care.
Learn the importance of early detection of breast cancer.
Overview of Breast Cancer Testing
Breast cancer testing involves several diagnostic tools designed to detect abnormalities in breast tissue. Each test plays a vital role in identifying potential problems early, when treatment is most effective.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of breast cancer saves lives. Regular screenings are especially important for those with higher risk factors, such as a family history of breast cancer or genetic predispositions. Detecting breast cancer in its earliest stages leads to:
- Better treatment outcomes
- Less invasive procedures
- Higher survival rates
Types of Breast Cancer Screening Tests
Your doctor will determine which types of breast cancer testing are right for you based on multiple factors, including age, breast density, risk factors, and previous breast cancer screening results. The most common breast cancer testing methods are:
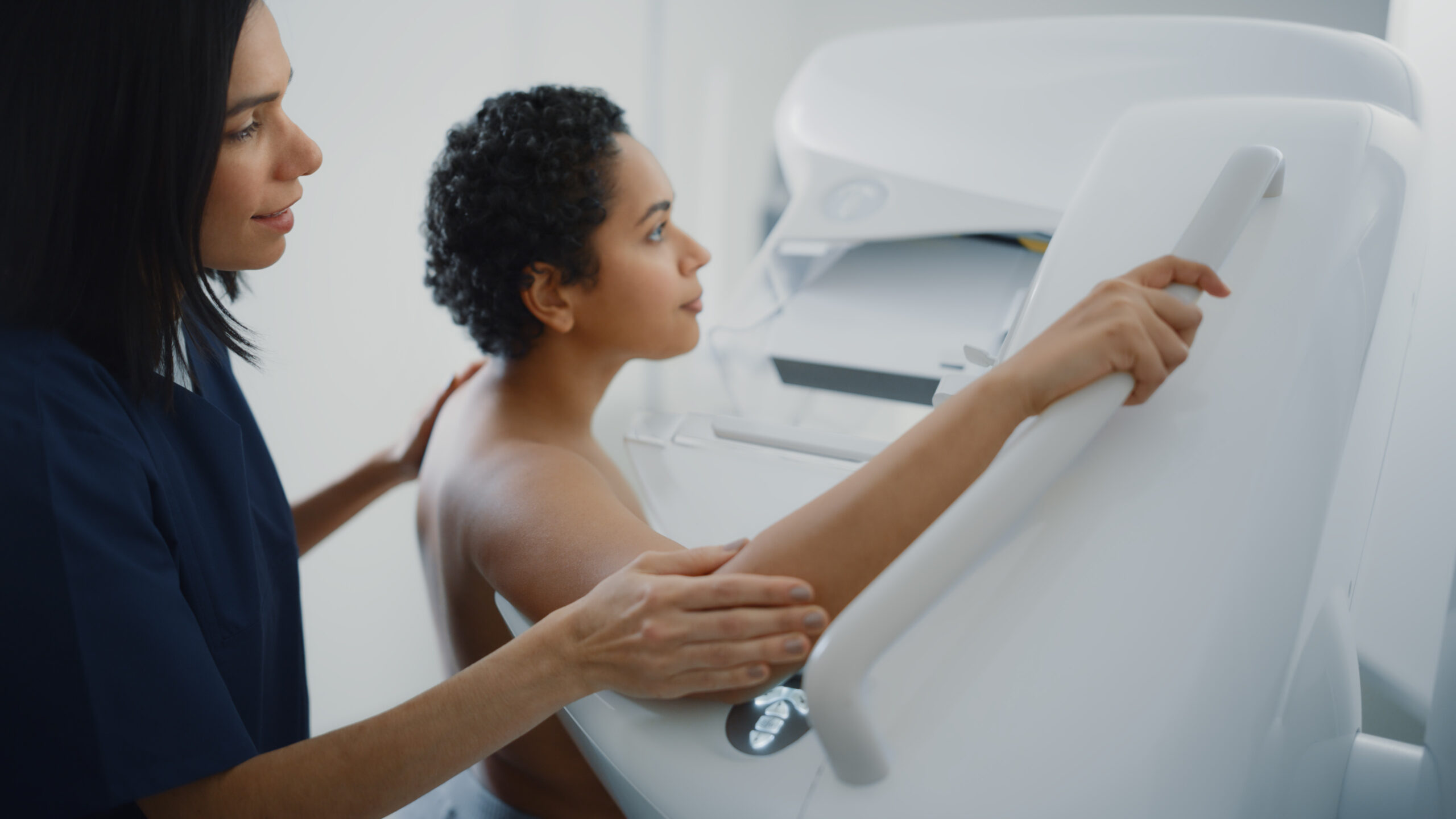
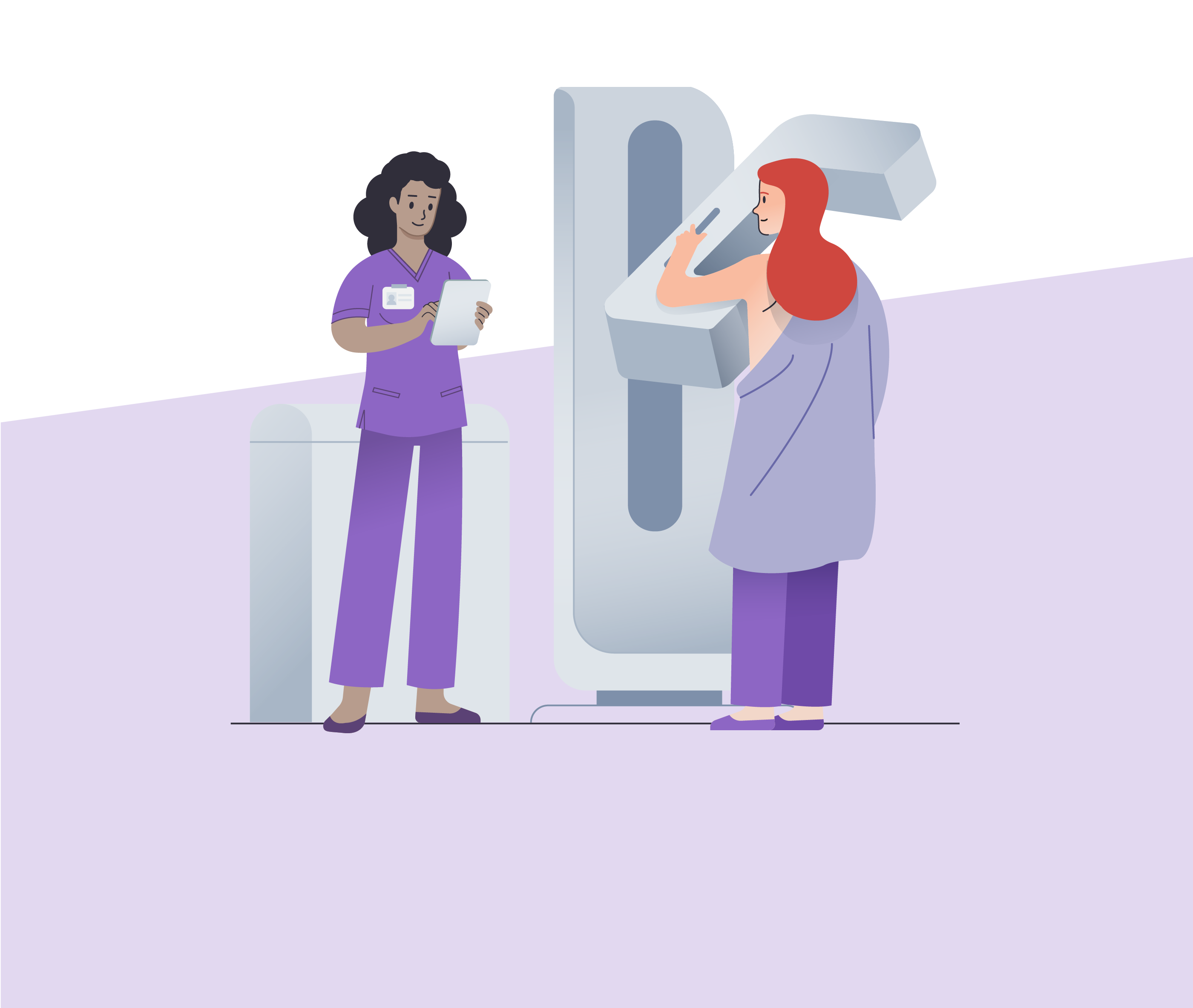
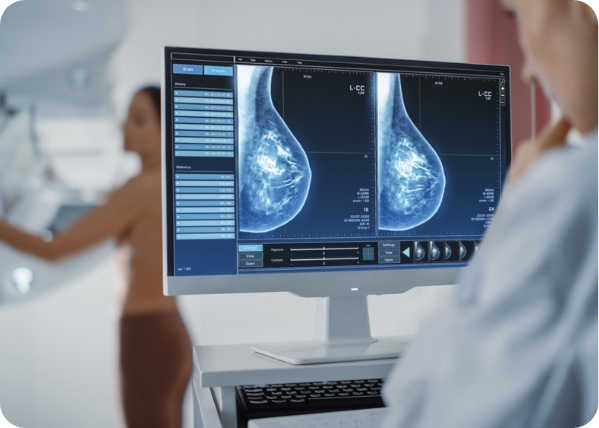
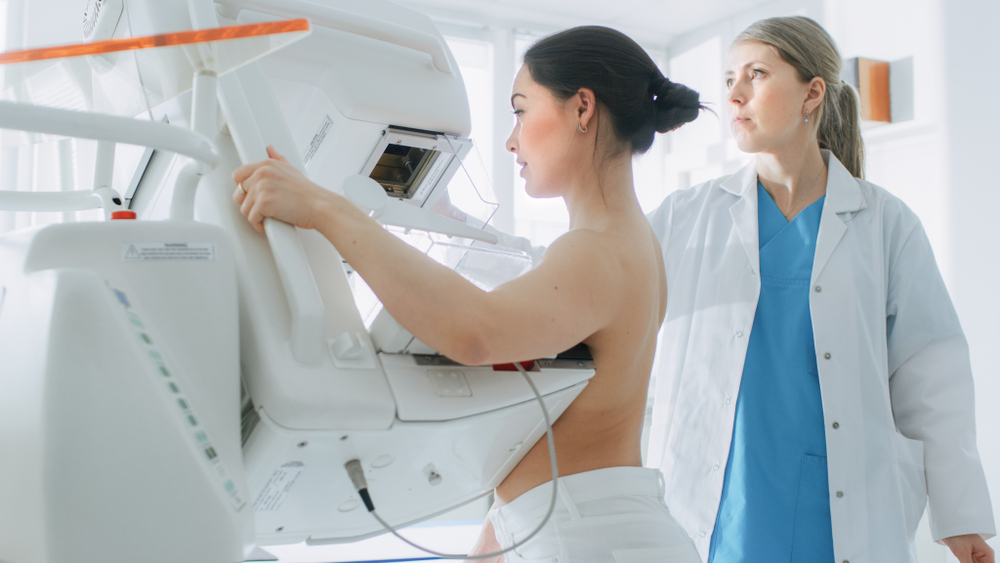
- Mammogram Testing: Considered the gold standard for breast cancer screening, mammograms use low-dose X-rays to detect changes in breast tissue before symptoms appear, making them highly effective for early detection.
- Breast Ultrasound: This non-invasive test provides additional clarity by using sound waves to generate images and is often used as a supplementary tool to mammograms, especially for women with dense breast tissue.
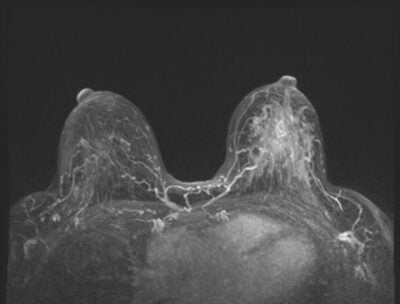
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scans: This more advanced screening option provides detailed images of the breast, making it an essential tool for those with high-risk factors like a strong family history of breast cancer or genetic mutations like BRCA1 and BRCA2.
- Breast Cancer Genetic Testing: Genetic testing is a critical step for individuals with significant family history or early diagnoses within the family, as it can identify mutations that increase the likelihood of developing breast cancer. This.
Understanding the Imaging Process
Knowing what to expect during breast screening tests can ease anxiety and help you prepare, physically and mentally.
What to Expect During Each Test
- Mammograms: During a mammogram, each breast is compressed between two plates to spread the tissue evenly and capture clear X-ray images. Although the compression may cause mild discomfort, the process is quick, usually lasting only a few minutes.
- Breast Ultrasound: A gel is applied to the skin to allow a handheld transducer to glide over the area. It’s painless and provides real-time images of the breast tissue.
- MRI: During an MRI, you will lie face down on a table with openings for your breasts. The table slides into the MRI machine, where detailed images are captured using magnetic fields. The procedure is non-invasive but may take 30 minutes or more.
When to Start Breast Cancer Screening
Breast cancer screening recommendations vary based on age, health, and risk factors. Collaborate with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan.
Average Risk:
- Women aged 40-45: Annual mammograms are typically recommended, and performed as early as age 25.
- Women aged 55+: Mammograms may be scheduled every two years, depending on preferences and health.
Higher Risk:
- Women with a family history of breast cancer, genetic mutations, or other risk factors may need to start screening at age 25.
- Additional tests, such as MRIs or genetic testing, may be suggested for more detailed assessments.
Interpreting Test Results and Next Steps
After your mammogram, you’ll receive a lay letter that explains your results in clear, simple terms. This letter summarizes key findings and a copy is also sent to your doctor for further review.
Components of a Lay Letter and What They Mean
A mammogram results letter contains a lot of crucial information including:
- Screening Outcome: Indicates if the results were normal or if further evaluation is needed.
- Breast Density: Notes whether you have dense breast tissue, which can affect mammogram accuracy.
- BI-RADS Score: Provides a numeric classification of findings (e.g., 1 for normal, 4-5 for suspicious).
Following Up on Your Results
By understanding your results and acting on them promptly, you take an important step in protecting your breast health. If your letter mentions abnormal findings or recommends additional imaging, there are a few steps you should take.
- Contact your doctor to schedule a discussion to review the results in detail.
- Plan follow-up tests such as diagnostic mammograms, ultrasounds, or MRIs.
- Ask Questions: Ensure you understand what the next steps entail and why they’re needed.
Stay Informed About Breast Cancer Awareness
Taking proactive steps toward breast cancer awareness is a powerful way to safeguard your health. Follow our women’s health blog for up-to-date information about breast cancer screening recommendations.
Resources




















![monitoring breast density shutterstock_1299510538-[Converted]](https://magview.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/shutterstock_1299510538-Converted.jpg)