Many of the top women’s health issues are preventable. Educate yourself about the most common female health problems so you can get appropriate screenings and prompt treatment to optimize your health outcomes.
Women’s Health Factors
There are several factors that influence how individuals experience specific women’s health problems.
Genetics
Genes alone do not determine your health outcomes, but they do play a role in determining risk factors. Knowing your family history can help your doctors to schedule appropriate health screenings to keep track of changes.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal changes are inevitable throughout a woman’s life. The menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and age-related changes like menopause all alter hormone levels. Hormonal imbalances don’t usually directly cause serious health conditions but they can impact stress levels, memoirs, concentration, headaches, weight, sleep, and other factors that put you at a higher risk for many health impairments.
Lifestyle / Diet
Your lifestyle and dietary choices have a great impact on your health and they are largely within your control. You can greatly improve your immune system function and your general physical and emotional wellbeing by:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Refraining from smoking, drinking, and drugs
- Getting enough sleep
- Exercising regularly
Understanding The Most Common Female Health Problems
There are many conditions that affect women’s health. This list represents some of the most common female health problems that you should be aware of and discuss with your doctor.
Menstrual Irregularities
Menstrual cycles vary by length and severity from woman to woman and may still be considered normal. Many changes to your menstrual cycle are short-term and not very serious, but menstrual irregularities can be a sign of a more serious health condition like pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease, uterine fibroids, or polycystic ovary syndrome. It’s important to let your doctor know if you experience any of the following:
- Bleeding that lasts more than a week
- Bleeding between periods
- Bleeding that is heavier than normal or results in soaking through pads or tampons every two hours or less
- Irregular periods when you are normally on a regular schedule
- Menstrual cycles more than 35 days apart or less than 21 days apart
- No bleeding for 90 days when you are not pregnant
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection (UTI), but they occur up to 30 times more often in women than in men. A woman’s urethra is shorter than a man’s and is close to the vagina and anus, the main sources of germs that get into the bladder and cause UTIs. A UTI can be painful but is easily treated with antibiotics. Some ways to prevent UTIs are:
- Wipe front to back
- Urinate before and after sex
- Drink plenty of water
- Wear cotton underwear
- Avoid tight fitting clothes
- Always urinate when you need to and avoid holding it for extensive periods of time
Yeast Infections
Up to 75% of women will get a yeast infection in their lifetime, with many women experiencing at least two yeast infections. A yeast infection is caused by an overgrowth of candida, a kind of yeast that normally exists in the vaginal area. Yeast infections are generally treated with medication. Symptoms of yeast infections include:
- Burning during sex or urination
- Swollen or red vagina
- Vaginal pain or soreness
- Vaginal rash
- Vaginal discharge that can be either watery or thick and white with no odor
- Itching in vulva or vagina
- Burning during intercourse or while urinating
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal imbalance where women have too much of the male hormone androgen. This causes symptoms such as excessive facial hair and body hair, ovarian cysts, male pattern baldness, irregular menstrual periods, and fertility problems. PCOS often runs in families and is usually treated with birth control hormones.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis causes tissue similar to that which lines the uterus to grow outside of the uterus, causing pain and fertility issues. Women with endometriosis often experience pain during menstrual periods, sex, and urination. Though endometriosis can be very painful and may often go undiagnosed, it is usually easily manageable with medical treatment.
Uterine Fibroids
Also called leiomyomas, uterine fibroids are common growths of the uterus that happen during the childbearing years. They often cause no symptoms and go away on their own, but you may notice:
- Lower back pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Constipation
- Menstrual periods become longer, painful, or more frequent
- Pain or pressure in the pelvic area
- Growing stomach area
- Difficulty with urination
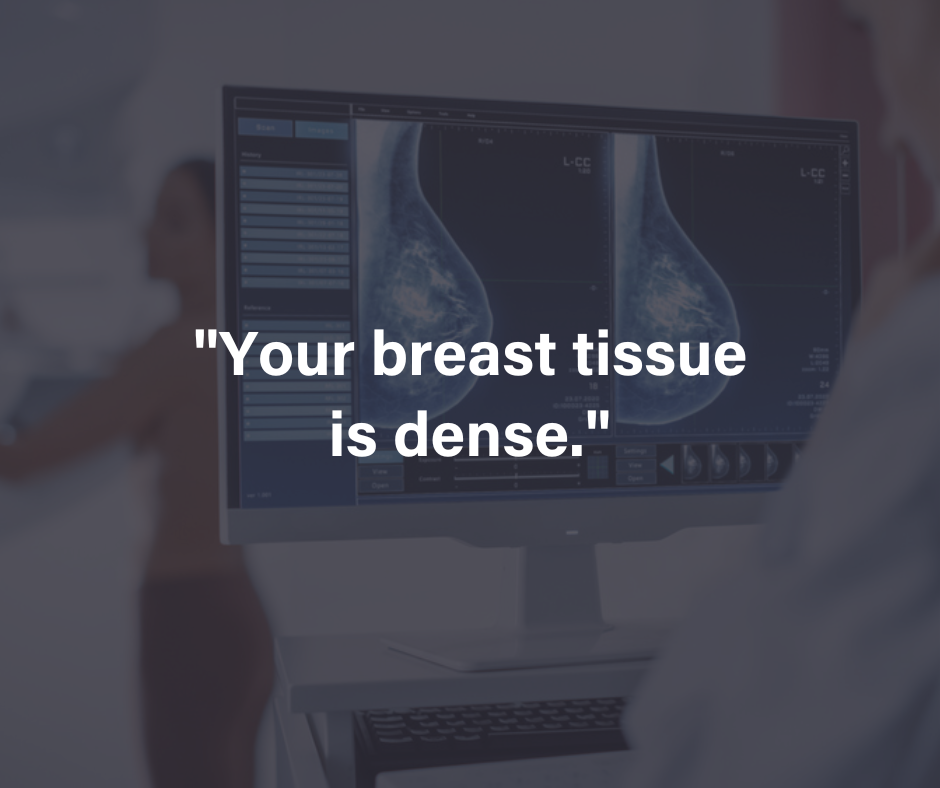
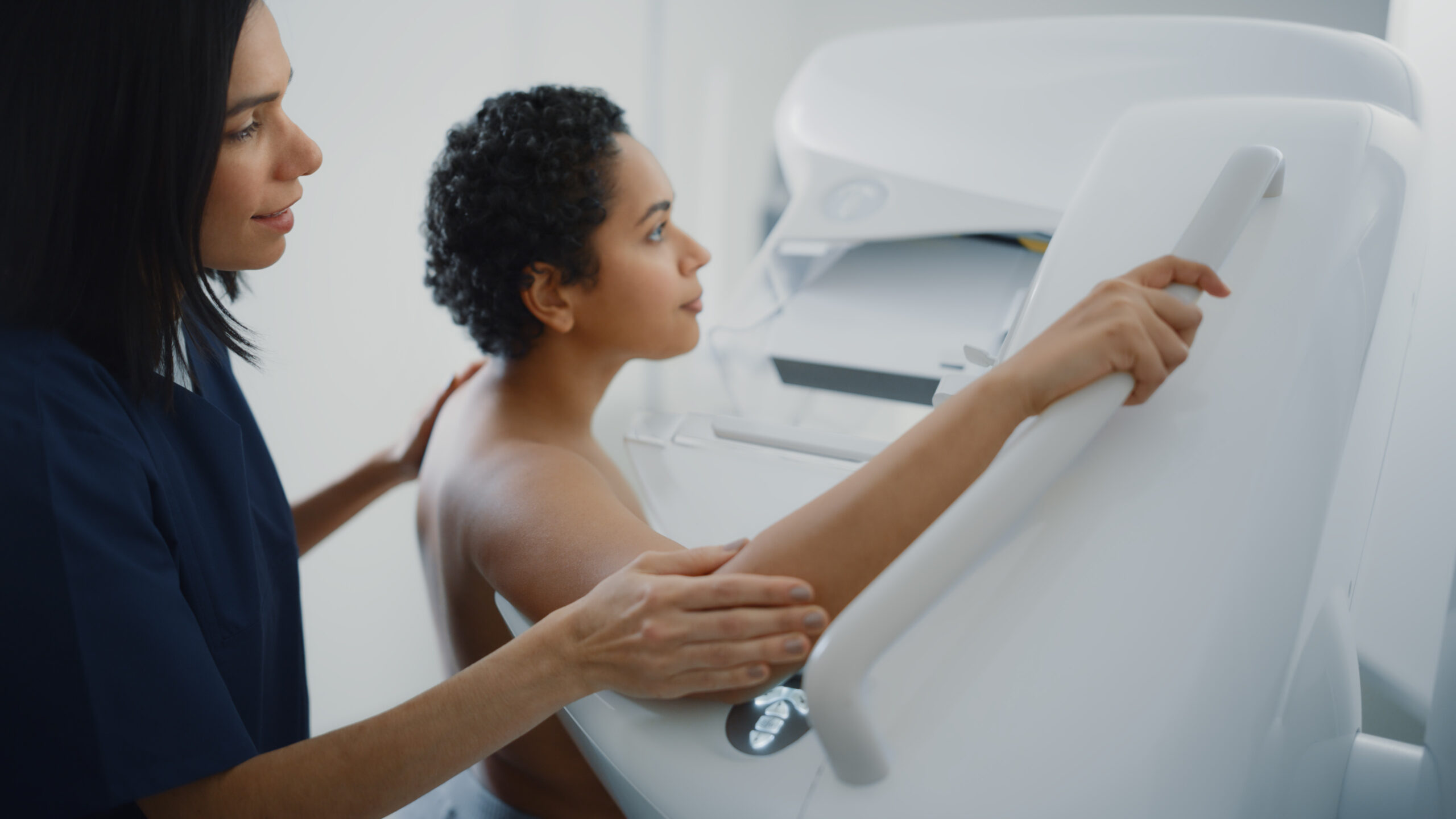
Breast Health
Breast pain and breast changes are not always serious, but it’s important to monitor breast health. Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women, but it is nearly 100% treatable when caught in its earliest stages. Be sure to follow breast screening recommendations and talk to your doctor if you notice:
- Changes to breast size and shape
- Changes or discharge from nipples
- Lumps in your breasts
- Swelling that lingers
- Reddened or thickened skin on your breast
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease that causes bones to become weak and break easily. Though not specific to women, older women in particular who are past menopause age are more susceptible to getting osteoporosis because estrogen loss weakens bones. Many people don’t know they have osteoporosis until their bones begin to break. Medicines and increased calcium and Vitamin may improve the effects of osteoporosis, but prevention is the best method. Talk to your doctor if you think you’re at risk for osteoporosis so they can do regular bone density tests and help you create a plan to strengthen your bones through diet and lifestyle choices.
Menopause and Perimenopause
Most women begin to notice the signs of transition to menopause (perimenopause) in their 40s. Perimenopause and menopause are both a normal part of aging, but they can cause distressing symptoms that may exacerbate or increase risk for other health conditions. Depending on the severity of your symptoms, you may not need medical attention, but you should talk to your doctor if any of the following symptoms are significantly impacting your life and health:
- Hot flashes
- Mood changes and irritability
- Irregular periods
- Vaginal dryness
- Fertility issues
- Bone loss
- Cholesterol changes
Reproductive Health Issues
Whether or not you have children or want to have children in the future, reproductive health matters. Regular gynecological care can include contraception, family planning, and fertility issues. If you are trying to get pregnant, it’s crucial to address your general health and risk factors to assure optimal outcomes for you and your future children.
Mental Health and Well-Being
Mental health is important for everyone, but women experience many mental health conditions differently than men do. Most serious mental health conditions do not have a cure, but their effects can be lessened and improved with medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. The most common mental health conditions in women are depression, eating disorders, and anxiety disorders.
Take Charge Of Your Health Today
The best way to improve your health outcomes is to educate yourself. Talk to your doctor about any concerns you have for your health and be sure to get all the recommended screenings for preventive care.













![monitoring breast density shutterstock_1299510538-[Converted]](https://magview.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/shutterstock_1299510538-Converted.jpg)